Kubernetes Deep Dive into its components.
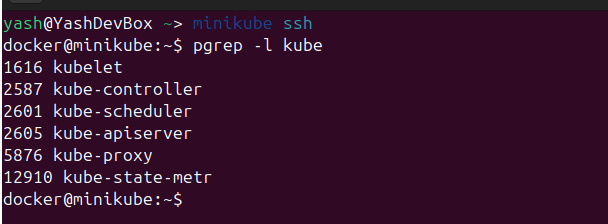
To understand the different components of the Kubernetes cluster we need to see what components are current running on the system. I have a minikube instance running and I can ssh into the instance to see all the processes that are running. For this I can run the following command.
docker@minikube:~$ minikube ssh
docker@minikube:~$ pgrep -l kube
docker@minikube:~$ pgrep -l etcd
Control Plane (Brain of the cluster)
As you can see that there are 6 main components. The kube-controller, kube-scheduler, kube-apiserver are part of the Control Plane which is the BRAIN of the Cluster.
kube-controller
Kube-Controller maintains the desired state of your cluster. It runs in a loop and follows the 3 steps.
- Observe
Checks the current state by calling the api server. - Compares Compares it wil the desired state
- Acts on the difference
It makes the current state back inline with the desired state.
kube-apiserver
- Front End API Exposes different endpoints which are accessed by various components. It also does validation, authentication of the requests and schema matching.
kube-scheduler
- Assigns the POD to the node It check for any new request by calling the kube-apiserver using the watch=true to get the new updates from the last time it called the endpoint. It then assigns the Node to the Pod. kubectl will then create the pod.
yash@YashDevBox:~$ TOKEN=$(kubectl create token default)
yash@YashDevBox:~$ echo $TOKEN
yash@YashDevBox:~$ APISERVER = $(kubectl config view --minify -o jsonpath='.clusters[0].cluster.server}')
yash@YashDevBox:~$ curl -N -s -K -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" "$APISERVER/api/v1/pods?watch=true"
etcd (Distributed Database of the Cluster)
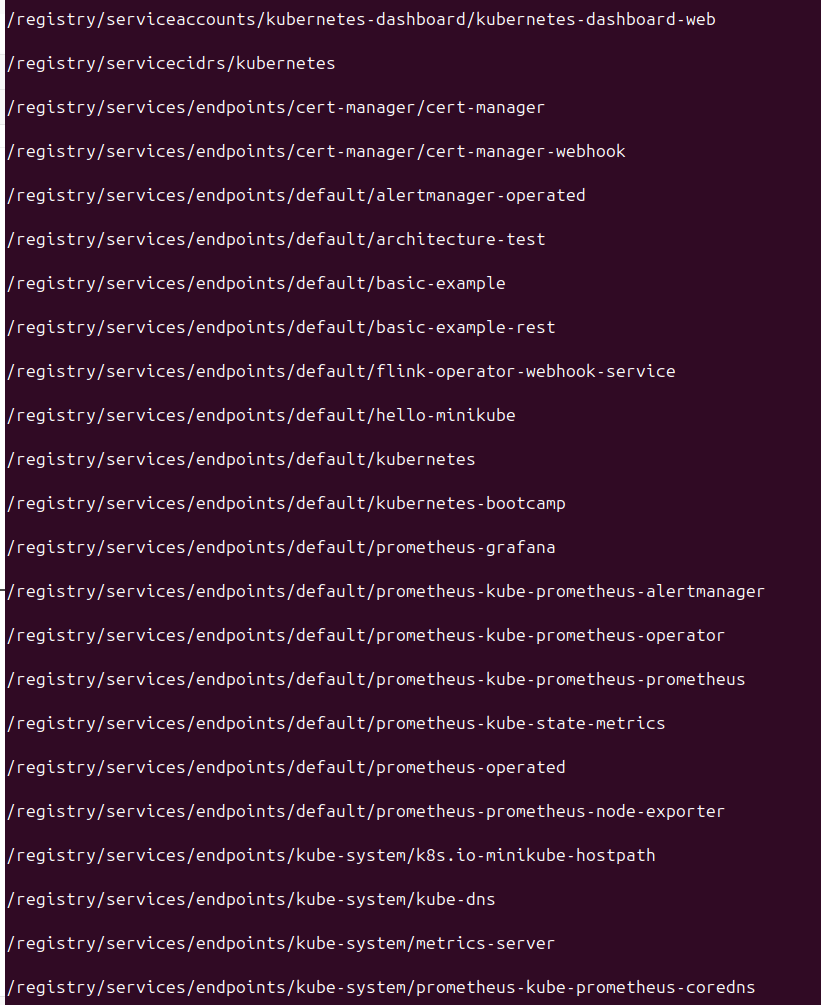
Along with this another component thats very critical is the etcd which is the Key-Value Pair database of the Cluster. This contains all the resource informations like the pods, nodes, configMaps, Secrets, services, CRD Custom Resource Definition.
yash@YashDevBox ~> kubectl get pods -n kube-system
yash@YashDevBox ~> kubectl describe pod etcd-minikube -n kube-system
yash@YashDevBox ~> kubectl exec -it etcd-minikube -n kube-system -- \
etcdctl --endpoints=https://127.0.0.1:2379 \
--cacert=/var/lib/minikube/certs/etcd/ca.crt \
--cert=/var/lib/minikube/certs/etcd/server.crt \
--key=/var/lib/minikube/certs/etcd/server.key \
get / --prefix --keys-only
You can view all the database keys/resources with the above commands.
kubectl (Systemd service)
kubectl is the systemd service and this is the first components that starts when the cluster is started. It looks at /etc/kubernetes/manifest folder and reads the yaml files and creates static pods for each of the component mentioned above.
docker@minikube:~$ sudo ls -laht /etc/kubernetes/manifests
If we add yaml files to manifests folder, the kubectl will create the resource for us bypassing the api-server. We can see the kube-controller yaml file and see that is part of the control-plane and that its a pod specifically static pods.
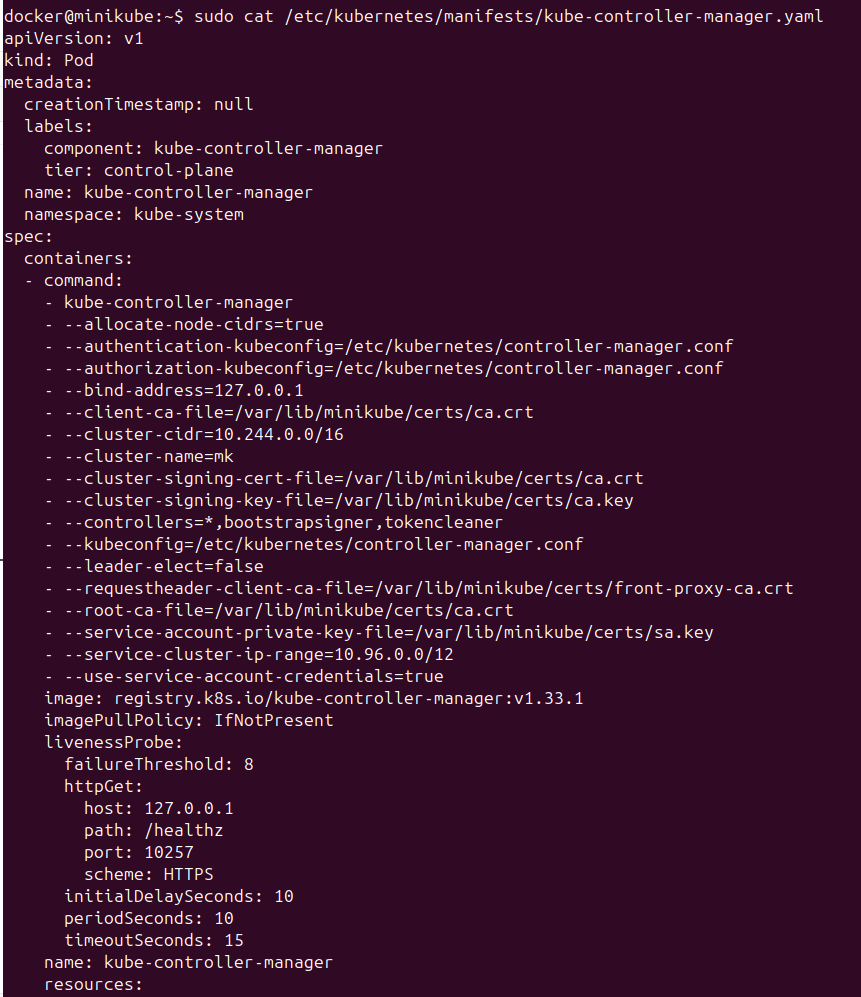
To recap, the below image makes all the concepts clear.
